Smart Coaching and Pose Analysis System
The Smart Coaching and Pose Analysis System is an advanced video-based solution designed to enhance training and performance evaluation by analyzing human poses in real-time. Leveraging computer vision and machine learning, this system extracts skeletal data from video feeds, compares coach and user movements, and provides actionable feedback for skill improvement in sports, fitness, or rehabilitation.
Architecture of created system
The following flowchart implemented and represent a sophisticated computer vision system that combines machine learning (YOLO, Detectron2) with traditional signal processing techniques (median and mean filtering) to analyze human movement in videos. Such systems are commonly used in applications like sports analysis, physical therapy assessment, security monitoring, or human-computer interaction research.
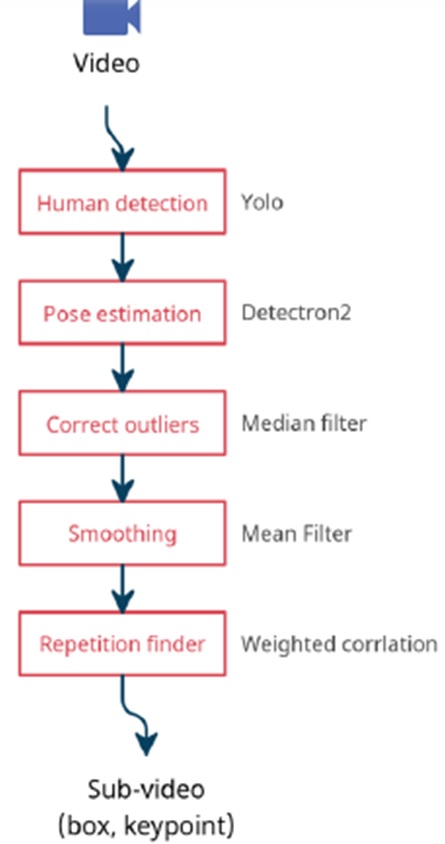
Processing Stages
Human Detection
- Uses YOLO (You Only Look Once) algorithm
- YOLO is a state-of-the-art, real-time object detection system that can identify people in video frames
- This stage identifies where humans appear in each video frame
Pose Estimation
- Employs Detectron2 framework
- Detectron2 is Facebook AI Research’s computer vision library that can identify human body keypoints
- This stage maps the skeletal structure of detected humans
Correct Outliers
- Implements a Median Filter
- This signal processing technique removes anomalous data points (outliers) from the detected keypoints
- Helps eliminate detection errors or jitter in the pose estimation
Smoothing
- Uses a Mean Filter
- This technique averages data points over time to create smoother motion trajectories
- Reduces noise in the keypoint movements
Repetition Finder
- Leverages Weighted Correlation
- This pattern recognition technique identifies recurring patterns in the processed data
- Likely used to detect repetitive movements or exercises
Output
- The final output is labeled as “Sub-video (box, keypoint)”
- This suggests the system produces video segments containing:
- Bounding boxes around detected humans
- Keypoints marking their skeletal joints/positions
Motion Comparison Flowchart
This flowchart illustrates a sophisticated system designed to compare human motion patterns between two subjects - a “Coach” and a “Student.” The system uses advanced computer vision and pattern recognition techniques to analyze and score movement similarities. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Input Sources
- Coach: Reference motion/movement (expert demonstration)
- Student: Subject motion/movement to be evaluated
- Processing Flow
Skeleton Analysis Both Coach and Student inputs undergo skeleton analysis. This process extracts skeletal pose information from video inputs Creates a structured representation of body positions and movements.
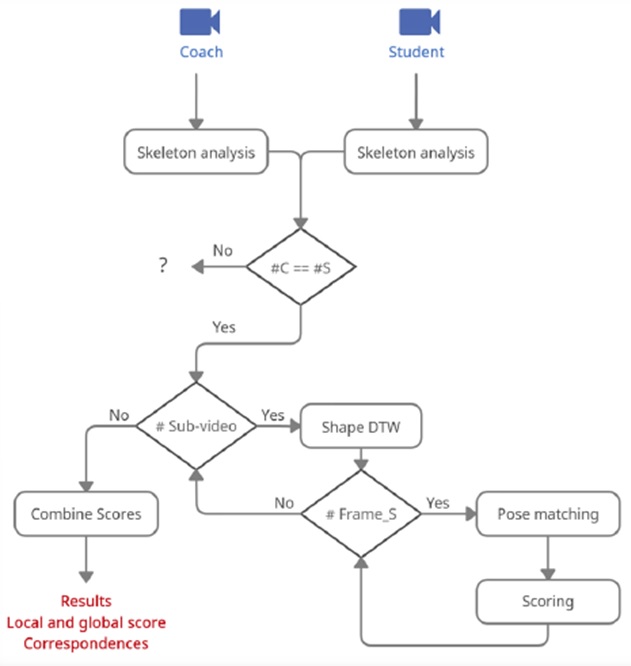
Initial Comparison (#C == #S) Checks if the number of detected skeletons or key components match between Coach and Student. This ensures a valid comparison can be made Sub-video Check If skeletons match, the system checks for the presence of sub-videos. Sub-videos likely represent segmented movement sequences
Shape DTW (Dynamic Time Warping) Applied when sub-videos are present. DTW is a powerful algorithm that aligns and compares time series data even when performed at different speeds Allows for meaningful comparison of movements that might be executed at different tempos
Frame Analysis (#Frame_S) Evaluates individual frames from the Student’s motion sequence. Creates a loop for frame-by-frame processing.
Pose Matching and Scoring Within the frame analysis loop:
- Matches corresponding poses between Coach and Student
- Assigns scores based on similarity/accuracy
- This creates detailed, frame-level evaluation
Score Combination After all frames are processed (or if no sub-videos were present). Combines individual scores into comprehensive metrics
Final Output
- Produces “Local and global score Correspondences”
- Local scores: Detailed evaluations of specific movements or time segments
- Global scores: Overall assessment of motion similarity
- Correspondences: Mapping between Coach and Student movements This system represents an advanced application of computer vision, pattern recognition, and signal processing techniques for human motion analysis. Such systems are valuable in contexts like: Sports training and coaching, Physical rehabilitation and therapy, Dance or martial arts instruction, Ergonomic movement assessment, Motion capture analysis. The integration of DTW is particularly significant as it allows for meaningful comparison even when movements are performed at different speeds or with slight timing variations.
Skeleton Extraction
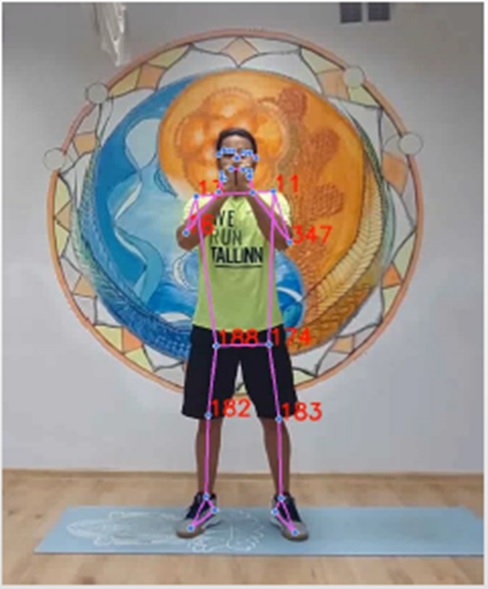

Comparing two video

Key Features and Benefits
This system utilizes state-of-the-art technology to deliver impactful capabilities for training and analysis:
- Real-Time Pose Estimation: Employs advanced algorithms like deep learning (e.g., Detectron2) to accurately track human skeletons from video input.
- Skeleton Extraction and Comparison: Extracts and compares skeletal movements between coach and user, identifying discrepancies for targeted feedback.
- Repetition and Pattern Analysis: Detects repetitive motions and evaluates performance consistency using weighted correspondence techniques.
- Actionable Feedback: Provides real-time scoring and pose-matching insights to enhance skill development and correct posture.
- Robust Data Processing: Integrates smoothing and outlier correction to ensure reliable analysis across varied conditions.
Applications and Impact
The system supports diverse applications with significant benefits:
- Sports Training: Assists athletes and coaches in refining techniques through precise pose analysis and comparison.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Monitors patient movements to ensure correct exercises, aiding recovery from injuries.
- Fitness Optimization: Helps fitness enthusiasts improve form and efficiency with real-time guidance.
- Educational Tools: Enhances learning environments by providing objective feedback on physical skills.
Technical Specifications
- Video Input: High-resolution cameras capturing real-time video feeds for pose detection.
- Pose Estimation Module: Utilizes Detectron2 and YOLO for human detection and skeletal tracking.
- Processing Pipeline: Includes median and mean filters for smoothing, outlier correction, and weighted correspondence analysis.
- Comparison Engine: Implements Shape DTW (Dynamic Time Warping) for comparing coach and user poses.
- Output Interface: Provides a dashboard with local and global scores for performance evaluation.
Research and Development
Developed by the Pattern Recognition Laboratory at Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, this system builds on cutting-edge research in computer vision and motion analysis to ensure accuracy and scalability.
Background and Importance
Effective training and rehabilitation rely on precise movement analysis. This system addresses the need for automated, real-time feedback in kinesiology and sports science, reducing human error and enhancing performance outcomes.
Project Implementation
The system integrates several key components for seamless operation:
- Video Input: Captures footage of coach and student, processed through human detection (YOLO) and pose estimation (Detectron2).
- Skeleton Extraction: Analyzes skeletal data from both coach and user, enabling detailed movement comparison.
- Processing Pipeline: Applies smoothing, outlier correction, and repetition finding to refine data accuracy.
- Comparison and Scoring: Uses Shape DTW and pose matching to evaluate movements, combining scores for final assessment.
- Feedback Generation: Outputs local and global scores, providing actionable insights for improvement.
Challenges and Solutions
- Accuracy in Variability: Advanced filtering and weighted correspondence address variations in lighting and movement speed.
- Real-Time Performance: Optimized algorithms ensure low-latency processing for immediate feedback.
- Data Privacy: Local processing minimizes data transmission, ensuring compliance with privacy standards.
Conclusion
The Smart Coaching and Pose Analysis System is a groundbreaking tool for enhancing training and rehabilitation. By integrating IoT, computer vision, and machine learning, it delivers precise, real-time feedback, fostering improved performance and safety across various domains.
